Database Management Systems
School of Computer Science, UPES
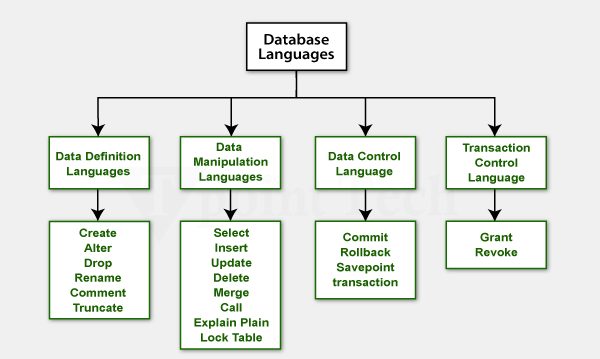
DBMS Languages Overview
📝 Data Definition Language (DDL)
- Used by DBA and database designers to specify the conceptual schema
- Defines internal and external schemas (views) in many DBMSs
- Some systems use separate SDL and VDL
- SDL typically realized via DBMS commands for DBA
🔄 Data Manipulation Language (DML)
- Used to specify database retrievals and updates
- Can be embedded in host languages (COBOL, C, C++, Java)
- Library functions can provide DBMS access
- Stand-alone DML commands (query language)
🔒 Data Control Language (DCL)
- Controls access to data and database objects
- Manages user permissions and privileges
- Ensures database security and authorization
- Main commands: GRANT, REVOKE
⚡ Transaction Control Language (TCL)
- Manages database transactions
- Ensures data consistency and integrity
- Controls transaction boundaries
- Main commands: COMMIT, ROLLBACK, SAVEPOINT
• DDL defines structure
• DML manipulates data
• DCL controls access
• TCL manages transactions
| Language Type | Purpose | Key Commands | Examples |
|---|---|---|---|
| DDL | Define database structure | CREATE, ALTER, DROP | CREATE TABLE, DROP INDEX |
| DML | Manipulate data | SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE | SELECT * FROM table |
| DCL | Control access permissions | GRANT, REVOKE | GRANT SELECT ON table TO user |
| TCL | Manage transactions | COMMIT, ROLLBACK, SAVEPOINT | COMMIT; ROLLBACK; |
Interactive Language Demo
Click the buttons above to see examples of DDL, DML, DCL, and TCL in action!
🔝 High-Level (Non-Procedural) Languages
Characteristics:
- Declarative: Specify WHAT you want, not HOW to get it
- Set-oriented: Operations work on entire sets of data
- Automatic optimization: DBMS determines best execution strategy
- User-friendly: Closer to natural language
- Less programming required: Focus on logic, not implementation
Examples:
- SQL: Standard query language for relational databases
- QBE (Query By Example): Visual query interface
- QUEL: Query language for INGRES DBMS
- Datalog: Logic-based query language
🔧 Low-Level (Procedural) Languages
Characteristics:
- Procedural: Specify HOW to retrieve data step-by-step
- Record-oriented: Operations work on one record at a time
- Manual navigation: Programmer controls data access path
- More complex: Requires detailed programming knowledge
- Direct control: Fine-grained control over operations
Examples:
- Network DML: CODASYL DBTG languages
- Hierarchical DML: IMS DL/I language
- Early file systems: ISAM, VSAM access methods
- Pointer-based navigation: Direct record addressing
⚖️ Comparison: High-Level vs Low-Level
| Aspect | High-Level (Non-Procedural) | Low-Level (Procedural) |
|---|---|---|
| Approach | Declarative - "What to get" | Procedural - "How to get" |
| Data Processing | Set-oriented operations | Record-at-a-time processing |
| Optimization | Automatic by DBMS | Manual by programmer |
| Ease of Use | User-friendly, less coding | Complex, more coding required |
| Performance | Generally efficient | Can be optimized manually |
| Portability | High (standardized) | Low (system-specific) |
🖥️ Stand-alone Query Interface
Direct SQL queries at DBMS interface (e.g., SQL*Plus in Oracle)
👨💻 Programmer Interfaces
Embedding DML in programming languages
📋 Menu-based Interfaces
Popular for web browsing, user-friendly navigation
📝 Forms-based Interfaces
Designed for naive users, structured data entry
🎨 Graphics-based Interfaces
Point and click, drag and drop functionality
🗣️ Natural Language Interface
Requests in written English
Interface Explanation
Click on any interface type above to learn more about it!
📊 Interface Types Summary
| Interface Type | Used By | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Stand-alone query | Advanced users | SQL*Plus, MySQL CLI |
| Programmer interface | Application programmers | JDBC, ODBC, Embedded SQL |
| Menu-based | Naïve users | ATM menus |
| Forms-based | Naïve users | Web forms, registration forms |
| Graphics-based | Naïve + intermediate | MS Access, phpMyAdmin |
| Natural language | Casual users | "Show students older than 20" |
| Speech/Browser/Parametric | Specialized | Voice queries, web apps, bank teller screens |
| DBA Interface | DBAs | Create accounts, manage schema |
🛠️ What are Database System Utilities?
Database utilities are software tools provided along with a DBMS to perform supporting tasks that make database management easier.
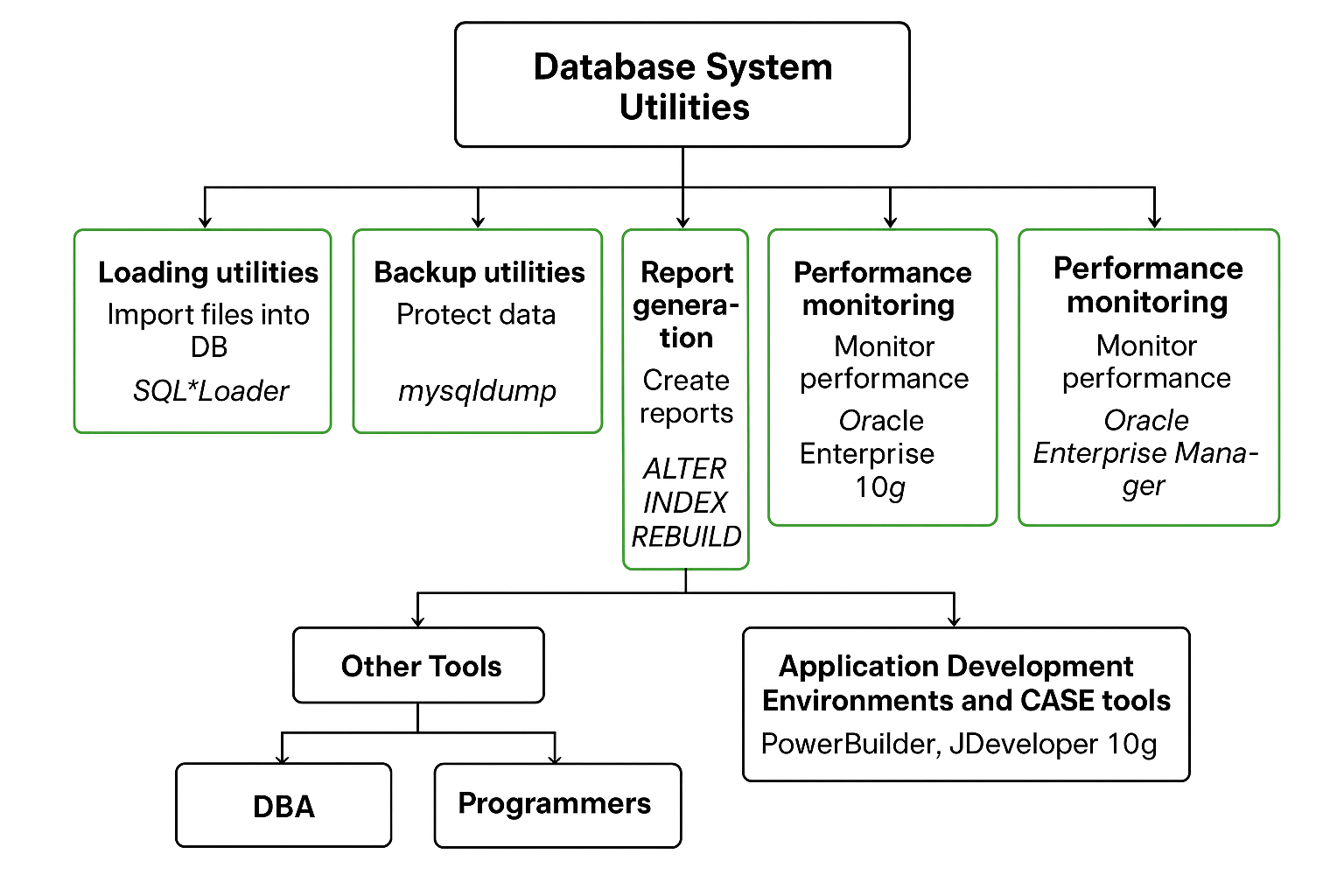
Database System Utilities Overview
📊 Loading Utilities
- Data Loading: Load existing data files into the database
- Bulk Loading: Efficiently load large volumes of data
- Format Conversion: Convert data from various file formats
- Data Validation: Check data integrity during loading
💾 Backup and Recovery Utilities
- Database Backup: Create copies of database for safety
- Incremental Backup: Backup only changed data
- Point-in-time Recovery: Restore database to specific time
- Transaction Log Backup: Backup transaction logs
📈 Performance Monitoring Utilities
- Query Performance: Monitor and analyze query execution
- Resource Usage: Track CPU, memory, and disk usage
- Lock Monitoring: Detect and resolve deadlocks
- Statistics Collection: Gather database performance metrics
🔧 Database Reorganization Utilities
- Index Rebuilding: Reorganize indexes for better performance
- Table Reorganization: Optimize table storage
- Space Management: Reclaim unused space
- Defragmentation: Reduce data fragmentation
🔍 Database Analysis Utilities
- Schema Analysis: Analyze database structure
- Data Profiling: Understand data quality and patterns
- Dependency Analysis: Track object dependencies
- Usage Statistics: Monitor database usage patterns
Utility Demonstration
Click the buttons above to see examples of different database utilities in action!
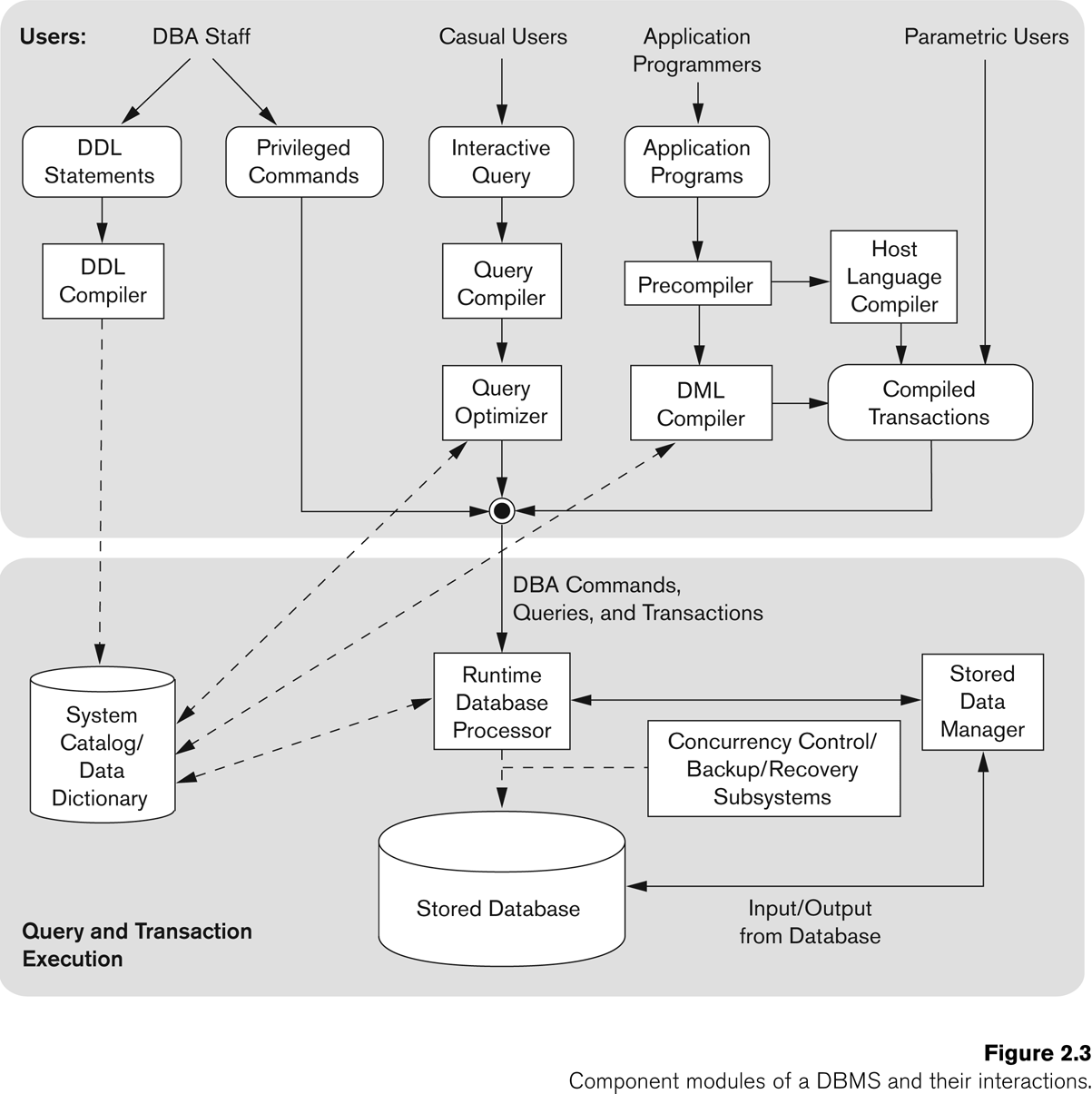
Typical DBMS Component Modules
🎯 Overview
A DBMS is not just a query processor — it has many components working together. The diagram groups them by Users (who interact) and Query/Transaction Execution Modules (how DBMS processes).
👥 Users of DBMS
DBA Staff (Database Administrators)
- Use DDL (Data Definition Language) statements → to define schema, create/alter tables, etc.
- Use Privileged commands → to manage users, authorizations, and storage structures.
Casual Users
- Write interactive queries (e.g., SQL queries directly in SQL*Plus, MySQL CLI).
Application Programmers
- Write application programs that embed SQL queries in a host language (like Java, C, Python).
Parametric Users
- Use predefined transactions repeatedly (e.g., bank tellers, ATM systems).
🏗️ DBMS Component Modules
1. DDL Compiler
- Converts DDL statements (like CREATE TABLE) into internal definitions.
- Stores them in the System Catalog / Data Dictionary (metadata repository).
2. System Catalog / Data Dictionary
- Stores metadata about the database:
- • Table definitions
- • Index info
- • Constraints
- • User permissions
- Essential for query processing.
3. Query Compiler
- Takes a query (like
SELECT * FROM Students WHERE Age>20;) and translates it into a low-level form (query plan).
4. Query Optimizer
- Improves the execution strategy for queries.
- Chooses best path: e.g., use index vs full table scan.
5. Precompiler
- Used when SQL is embedded inside a programming language (like C, Java).
- Extracts SQL commands and sends them to the DML compiler.
- Leaves the rest of the program for the host language compiler.
6. DML Compiler
- Translates DML statements (like SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE) into low-level instructions for the runtime database processor.
7. Host Language Compiler
- Compiles the application program (C, Java, etc.) with calls to the DBMS.
- Produces compiled transactions.
8. Runtime Database Processor
- Core module that executes DBA commands, queries, and transactions.
- Interacts with:
- • Stored Database (physical data on disk)
- • Concurrency Control & Recovery Subsystems
9. Concurrency Control / Backup / Recovery Subsystems
- Ensure correctness, consistency, and reliability of transactions:
- • Concurrency Control → handles multiple users at once.
- • Backup → periodic saving of database.
- • Recovery → restores database after failure.
10. Stored Database
- The actual physical data on disk.
11. Stored Data Manager
- Manages the input/output operations between DBMS and physical storage.
- Ensures efficiency of file access, buffering, indexing.
✅ Summary Flow
DDL Statements → DDL Compiler → Data Dictionary
Interactive Queries → Query Compiler → Query Optimizer → Runtime Processor
Application Programs → Precompiler + Host Language Compiler + DML Compiler → Compiled Transactions → Runtime Processor
Runtime Processor → Stored Database + Concurrency/Recovery Systems
Front-end modules (DDL compiler, Query compiler, DML compiler) → translate user requests.
Back-end modules (Runtime processor, Data manager, Recovery/Concurrency) → execute and manage data safely.
Content loading...
Content loading...
Content loading...