Algorithms, Pseudocode & Flowcharts
Topic: Problem-solving techniques using algorithms, pseudocode, and flowcharts
Course: C Programming Fundamentals
📚 Lecture Details
Prepared by: Dr. Mohsin F. Dar
Designation: Assistant Professor, School of Computer Science
Institution: UPES, Dehradun
Target Audience: B.Tech-CSE-I-B47 and B.Tech-CSE-I-B48
🎯 Learning Objectives
By the end of this lecture, students will be able to:
- Understand the concept and importance of algorithms in problem-solving
- Write clear and structured pseudocode for various problems
- Create flowcharts using standard symbols and conventions
- Compare and choose appropriate problem-solving methods
- Apply these techniques to solve real-world programming problems
- Analyze the efficiency and clarity of different approaches
🔍 What is an Algorithm?
Definition: An algorithm is a step-by-step procedure or set of rules designed to solve a specific problem or perform a particular task.
Key Characteristics of Algorithms:
🎯 Well-defined
Each step must be clear and unambiguous
📥 Input
Takes zero or more inputs
📤 Output
Produces at least one output
⏰ Finite
Must terminate after finite steps
✅ Effective
Each step must be feasible and executable
🔄 Deterministic
Same input produces same output
📝 Algorithm Example: Finding Maximum of Three Numbers
Algorithm Steps:
- START
- INPUT: Read three numbers A, B, and C
- INITIALIZE: Set MAX = A
- COMPARE: If B > MAX, then set MAX = B
- COMPARE: If C > MAX, then set MAX = C
- OUTPUT: Display MAX as the largest number
- STOP
🔍 Analysis:
- Input: Three numbers (A, B, C)
- Output: Maximum value among the three
- Steps: 7 clear, executable steps
- Efficiency: O(1) - constant time
📋 What is Pseudocode?
Definition: Pseudocode is a high-level description of a computer program's logic that uses natural language mixed with programming constructs.
Advantages of Pseudocode:
- Language Independent: Not tied to any specific programming language
- Easy to Understand: Uses natural language constructs
- Quick to Write: Faster than actual code development
- Easy to Modify: Changes can be made quickly
- Bridge: Connects problem analysis to code implementation
Common Pseudocode Conventions:
BEGIN / START - Start of algorithm END / STOP - End of algorithm INPUT / READ - Input operation OUTPUT / PRINT - Output operation SET / ASSIGN - Assignment operation IF...THEN...ELSE - Conditional statements WHILE...DO - Loop statements FOR...TO...DO - Loop statements REPEAT...UNTIL - Loop statements
📝 Pseudocode Example: Same Problem
BEGIN FindMaximum
INPUT A, B, C
SET MAX = A
IF B > MAX THEN
SET MAX = B
END IF
IF C > MAX THEN
SET MAX = C
END IF
OUTPUT "The maximum number is: ", MAX
END FindMaximum
🎯 Benefits:
- Clear structure and logic
- Easy to convert to any language
- Readable by non-programmers
🔄 Translation to C:
This pseudocode can be easily translated to C, Python, Java, or any other programming language.
📊 What are Flowcharts?
Definition: A flowchart is a graphical representation of an algorithm that uses standard symbols to represent different types of operations and the flow of control.
Standard Flowchart Symbols:
Oval: Start and End points
Rectangle: Process / Action steps
Diamond: Decision / Condition
Parallelogram: Input / Output operations
Circle: Connector (jumps to another part of flow)
Curved Rectangle: Document / Report
Double-Rectangle: Predefined process / Subroutine
Flow Direction:
Arrows indicate the direction of flow. Example: START → PROCESS → DECISION? → YES/NO paths
📊 Flowchart Example: Finding Maximum
YES: MAX = B NO: Skip
YES: MAX = C NO: Skip
🔄 Comprehensive Example: Sum of First N Natural Numbers
📝 Algorithm
- START
- INPUT N
- SET SUM = 0
- SET I = 1
- WHILE I ≤ N DO
- SUM = SUM + I
- I = I + 1
- END WHILE
- OUTPUT SUM
- STOP
📋 Pseudocode
BEGIN SumNaturalNumbers
INPUT N
SET SUM = 0
SET I = 1
WHILE I <= N DO
SET SUM = SUM + I
SET I = I + 1
END WHILE
OUTPUT "Sum is: ", SUM
END SumNaturalNumbers
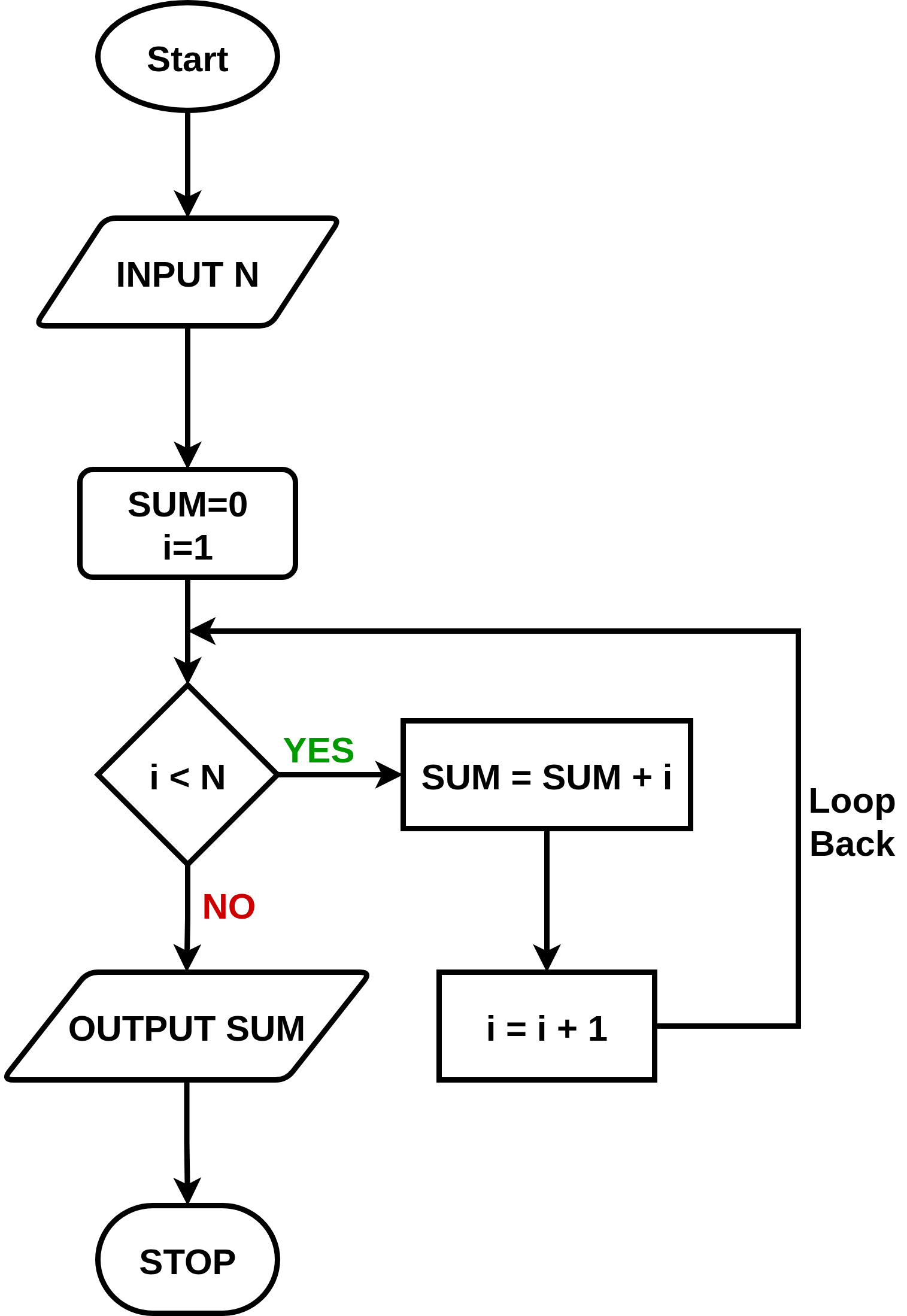
📝 Example Trace (N = 5):
Iteration 1: I=1, SUM=0+1=1
Iteration 2: I=2, SUM=1+2=3
Iteration 3: I=3, SUM=3+3=6
Iteration 4: I=4, SUM=6+4=10
Iteration 5: I=5, SUM=10+5=15
Final: I=6 > N=5, so OUTPUT SUM = 15
⚖️ Comparison: Algorithm vs Pseudocode vs Flowchart
| Aspect | Algorithm | Pseudocode | Flowchart |
|---|---|---|---|
| Format | Step-by-step text | Structured text with keywords | Graphical symbols |
| Ease of Understanding | Good for logical thinkers | Easy for programmers | Visual, easy for everyone |
| Detail Level | High-level overview | Medium detail | Visual flow representation |
| Modification | Easy to modify | Very easy to modify | Requires redrawing |
| Space Required | Compact | Compact | More space needed |
| Best For | Problem analysis | Code planning | Visual communication |
🎯 When to Use Each Method?
📝 Use Algorithms When:
- Initial problem analysis
- Documenting solution approach
- Communicating with non-technical stakeholders
- Breaking down complex problems
- Academic or theoretical discussions
📋 Use Pseudocode When:
- Planning code structure
- Team collaboration
- Code reviews and discussions
- Language-independent design
- Teaching programming concepts
📊 Use Flowcharts When:
- Visual learners in audience
- Complex decision structures
- Process documentation
- System design presentations
- Debugging logic flow
Best Practice: Use all three methods complementarily! Start with an algorithm for problem understanding, create pseudocode for implementation planning, and draw flowcharts for visual verification and communication.
💪 Practice Problems
Problem 1: Basic
Calculate the factorial of a number
Input: A positive integer N
Output: N! (N factorial)
Problem 2: Intermediate
Check if a number is prime
Input: A positive integer N
Output: "Prime" or "Not Prime"
Problem 3: Advanced
Sort an array using bubble sort
Input: Array of integers
Output: Sorted array in ascending order
Assignment: For each problem, create:
- A detailed algorithm with numbered steps
- Structured pseudocode with proper keywords
- A complete flowchart with standard symbols
📚 Summary
Key Takeaways:
- Algorithms provide step-by-step problem-solving procedures
- Pseudocode bridges the gap between algorithms and actual code
- Flowcharts offer visual representation of program logic
- Each method has its strengths and appropriate use cases
- Practice with all three methods improves problem-solving skills
🎯 Next Steps:
- Practice the assigned problems
- Start with simple problems and gradually increase complexity
- Compare your solutions with classmates
- Begin implementing pseudocode in C programming
📖 Remember:
- Think before you code
- Plan your solution approach
- Use the method that best fits your audience
- Practice makes perfect!